With the increasing awareness of health, everyone attaches great importance to physical health. According to health reports, osteoarticular problems (those relating to, involving, or affecting bones and joints) have imperceptibly become one of the top ten problems plaguing national health. Osteoarticular problems are also beginning to impact younger citizens as well including those born in the 90s and even the 00s.
Under such circumstances, an increasing number of people have become aware of the necessity of maintaining their bones and are willing to buy some health products with related functions for health care, among which glucosamine products are becoming the most prevalent.
What is glucosamine? And what is its function?
Glucosamine is a chemical compound (as shown in Figure 1) that is formed when a hydroxyl radical of glucose is replaced by an amino radical. Since glucosamine with an active group of amino radicals is chemically unstable, the glucosamine compounds commonly used in the market are mainly in the form of glucosamine hydrochloride and glucosamine sulfate as well as the double salts.
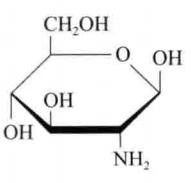
Figure 1 Chemical structure formula of glucosamine
As an important part of cartilage tissue, glucosamine can be widely found in the cartilage tissue of human and animal joints, to maintain the normal function of joint cartilage. However, the body's ability to synthesize glucosamine grows weaker with age, as a result, we continue to lose glucosamine. In middle age, such loss will be accelerated, which may easily lead to joint discomfort and various related diseases[1].
Actually, a large amount of glucosamine can be consumed in daily activities and sports. To sum up, in order to maintain bone health, a boost of glucosamine is essential, and it is sensible to replenish glucosamine before it is too late.
Exogenous supplementation with glucosamine can help people regulate their body functions. Several studies have shown that glucosamine has a significant effect on bone health maintenance, antioxidation, and immune regulation. In the area of maintaining bone health[2-4]:
- It can promote the synthesis of proteoglycans in cartilage tissue and maintain the normal structure of joint cartilage.
- It can improve osteoporosis by increasing the differentiation of osteopontin and osteocalcin in osteoblasts and accelerating osteocalcin deposition.
- It can inhibit the synthesis of certain inflammatory factors and exert anti-inflammatory effects.
The application of glucosamine in health food
As glucosamine can only be found in the shell of shrimps and crabs, the consumption of glucosamine in daily diet is quite small. The intake of glucosamine mainly comes from dietary supplements[5]. Currently, glucosamine-based substances have been approved and applied in several countries both at home and abroad, such as the United States, Canada, and Australia[1].
China
In China, glucosamine-based substances have been used as health food raw materials for many years, with the earliest approved products dating back to 1999.
According to data collected from the special food information query platform of the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR), as of November 20, 2022, there are 305 health food products containing glucosamine-based substances in China. These products are mainly used to increase bone density and promote bone health. “Increasing bone density” is the main health function, which accounts for about 90% of all approved registered products. In addition, glucosamine health food seldom exists as single-party products. Glucosamine is generally used together with chondroitin sulfate, calcium, and other raw materials.
The United States
In the United States, glucosamine hydrochloride/sulfate is listed as a dietary supplement ingredient. The United States Pharmacopeia (USP) includes standards for glucosamine hydrochloride, glucosamine sulfate-potassium chloride, and glucosamine sulfate-sodium chloride[6].
Canada
Canada lists glucosamine hydrochloride/sulfate as a Canadian natural health product that can be used as a dietary supplement. Products with glucosamine hydrochloride/sulfate can claim the function of maintaining cartilage health and contributing to joint health [7, 8].
Australia
Australia has included glucosamine sulfate-sodium chloride, glucosamine sulfate-potassium chloride, and glucosamine hydrochloride in the list of complementary medicines that can be used as raw materials for health food [9].
Is it safe to consume glucosamine-based substances?
Glucosamine exists in the human body and has been used safely for many years in the field of drugs and health food in China. Glucosamine-based substances also work safely as a dietary supplement raw material in the United States and other countries for many years. Besides, the raw material sources and preparation process of glucosamine hydrochloride/sulfate used in the United States are basically similar to those of China.
A number of safety trials on glucosamine have been conducted by both domestic and foreign scholars, and the results are basically consistent, confirming that glucosamine is in good safety with no acute toxicity, genotoxicity, and subacute toxicity, low incidence of adverse reactions, and the results of all the studies are optimistic[10, 11]. The CHINESE DIETARY REFERENCE INTAKES (2013 Edition) states that a daily intake of 1500 milligrams (mg) of glucosamine sulfate/hydrochloride (containing approximately 1000 mg of glucosamine) has shown significant biological effects in most clinical trial studies, with no significant adverse effects.
Therefore, in general, glucosamine-based substances are relatively safe with a low probability of causing side effects and can be widely used as health food raw materials.
Industry prospects
Nowadays, glucosamine has been widely used as health food raw materials worldwide. Glucosamine-related products are leading a sales volume in both major offline markets and e-commerce platforms for health food. However, the raw materials of glucosamine have not been included in the health food raw materials directory in China and there are no related national food safety standards as well as unified product technical requirements. In the registration of glucosamine health food, the principle of “one product, one standard” is adopted for the evaluation and approval of glucosamine-based health food.
Recently, the SAMR and National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China released a number of responses to the proposals on the inclusion of glucosamine in the new food raw materials directory and health food raw materials directory. These replies pointed out that, according to the evaluation and approval of the product technical requirements, combined with the preliminary research on the quality standards, safety, dosage, and allowable claims of health functions of glucosamine-based raw materials, with the efforts of relevant departments, SAMR will formulate the raw materials standards and technical requirements for glucosamine-based health food and positively promote the inclusion of glucosamine-based raw materials into the health food raw materials directory.
In other words, glucosamine-based raw materials are expected to be included in the health food raw materials directory as soon as possible and can be managed according to the health food filing system similar to coenzyme Q10, melatonin, fish oil, and other raw materials.
If you need any assistance or have any questions, please get in touch with us via service@hfoushi.com.

